Understanding the difference between the present perfect vs. past simple tenses is essential for mastering English grammar. Both tenses are used to talk about past events, but they serve different purposes and convey different nuances.
What is the Present Perfect Tense?
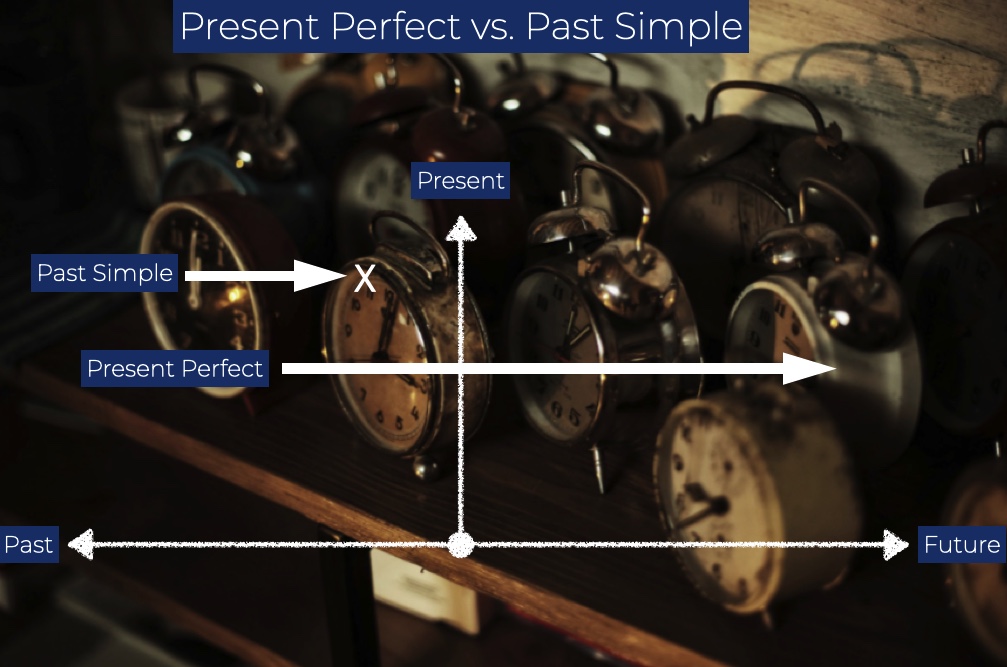
The present perfect tense is used to link past actions or events to the present. It is formed using the auxiliary verb “have” or “has” followed by the past participle of the main verb.
How is the Present Perfect Tense Used?
The present perfect tense is used to describe:
- Actions that occurred at an unspecified time before now.
- Actions that started in the past and continue to the present.
- Recent actions that have an effect on the present moment.
Examples:
- I have finished my homework. (Action completed at an unspecified time)
- She has lived in London for five years. (Action that started in the past and continues)
- They have just arrived. (Recent action with a present effect)
What is the Past Simple Tense?
The past simple tense is used to describe actions or events that were completed at a specific time in the past. It is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of regular verbs or using the second form of irregular verbs.
How is the Past Simple Tense Used?
The past simple tense is used to describe:
- Actions completed at a definite time in the past.
- Actions that occurred in a sequence.
Examples:
- I finished my homework yesterday. (Action completed at a specific time)
- She lived in London last year. (Action completed in the past)
- They arrived and then ate dinner. (Sequence of actions)
When to Use Present Perfect vs. Past Simple
Present Perfect
Use the present perfect when the exact time of the action is not important, when the action has relevance to the present moment, or when discussing life experiences.
Examples:
- I have traveled to Japan. (Life experience)
- He has lost his keys. (Relevance to the present)
- We have known each other since 2010. (Ongoing action)
Past Simple
Use the past simple when the exact time of the action is specified or implied, or when discussing actions that are no longer connected to the present.
Examples:
- I traveled to Japan last year. (Specific time)
- He lost his keys yesterday. (Specific time)
- We knew each other when we were kids. (Past action no longer ongoing)
What’s your English level?
Discover your level now: A1/A2/B1/B2/C1/C2 and GET your certificate!
Examples of Present Perfect vs. Past Simple
Present Perfect: She has visited Paris several times.
Past Simple: She visited Paris last summer.
Present Perfect: I have never seen that movie.
Past Simple: I saw that movie last night.
Present Perfect: We have completed the project.
Past Simple: We completed the project yesterday.
Present Perfect: They have moved to a new house.
Past Simple: They moved to a new house last month.
Present Perfect: He has worked here since 2015.
Past Simple: He worked here from 2015 to 2018.
Present Perfect vs. Past Simple Exercises
- I ________ (see) that movie before.
- She ________ (go) to the store an hour ago.
- They ________ (live) in New York for five years.
- We ________ (finish) our homework last night.
- He ________ (never/try) sushi before.
- You ________ (already/meet) him.
- We ________ (not/see) her since last year.
- She ________ (buy) a new car last week.
- They ________ (visit) the museum many times.
- I ________ (just/hear) the news.
Answers:
- have seen
- went
- have lived
- finished
- has never tried
- have already met
- have not seen
- bought
- have visited
- have just heard
By understanding when and how to use the present perfect and past simple tenses, you can improve your English communication skills and convey your messages more accurately. Use this guide to help you master these essential tenses!





