English is a truly global language, and with it comes a rich diversity of accents. In this blog post, we listed All English Accents Explained. From the rolling R’s of Scotland to the nasal tones of New York City, English accents vary greatly based on geography, culture, and history.
In this guide, we’ll explore the most prominent English accents around the world, their origins, unique features, and how they influence global English learning and usage.
🌍 Why Do English Accents Vary?
Accents are shaped by:
- Regional languages and dialects
- Migration and colonization
- Social class and education
- Media and globalization
Even within the same country, accents can differ dramatically from city to city — and sometimes street to street.
🇬🇧 British English Accents
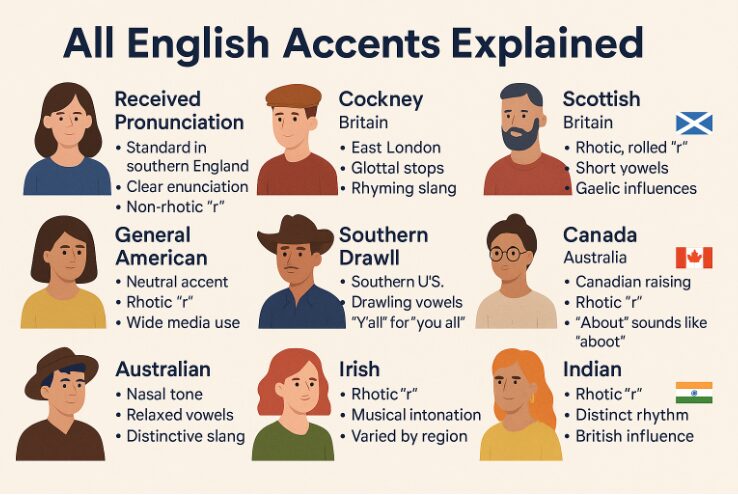
1. Received Pronunciation (RP) – “The Queen’s English”
- Region: Southern England (standardized)
- Features: Clear enunciation, non-rhotic (no “r” sound at end of words)
- Used in: BBC news, formal education, British drama
2. Cockney
- Region: East London
- Features: Glottal stops (“bu’er” instead of “butter”), rhyming slang
- Example: “Apples and pears” = stairs
3. Estuary English
- Region: Southeast England (Thames Estuary)
- Features: Mix of RP and Cockney, more relaxed pronunciation
- Widely used in modern media and business
4. Scouse
- Region: Liverpool
- Features: Rising intonation, nasal tones, unique vocabulary
- Distinct and highly recognizable
5. Geordie
- Region: Newcastle and Northeast England
- Features: Strong “oo” sounds, unique local vocabulary
- Example: “Howay man” = come on!
6. Yorkshire
- Region: Northern England
- Features: Flat vowels, use of old Norse-influenced words
- Known for its warmth and clarity
7. Scottish English
- Region: Scotland
- Features: Rolled “r”, shorter vowels, Gaelic influences
- Varied across cities like Glasgow, Edinburgh, Aberdeen
8. Welsh English
- Region: Wales
- Features: Musical intonation, vowel emphasis
- Influence of the Welsh language
What’s your English level?
Discover your level now: A1/A2/B1/B2/C1/C2 and GET your certificate!
🇺🇸 American English Accents
1. General American (GenAm)
- Region: Midwest, parts of the West
- Features: Neutral tone, rhotic (pronounced “r”)
- Most commonly used in TV and film
2. Southern Drawl
- Region: Southern U.S. (Texas, Georgia, etc.)
- Features: Drawn-out vowels, slow speech rhythm
- Example: “Y’all” for “you all”
3. New York City Accent
- Region: NYC, parts of New Jersey
- Features: Dropped “r”, sharp intonation (“cawfee” for coffee)
- Iconic in media
4. Boston Accent
- Region: Massachusetts (Boston area)
- Features: Non-rhotic, “pahk the cah” instead of “park the car”
5. Midwestern Accent
- Region: Illinois, Ohio, Wisconsin
- Features: Clear vowels, seen as “neutral” by many Americans
6. African American Vernacular English (AAVE)
- Region: Urban centers across the U.S.
- Features: Unique grammar, vocabulary, and rhythm
- Deep cultural roots in Black American communities
🇨🇦 Canadian English
- Region: Nationwide
- Features: Shares GenAm traits + unique vowel shift (e.g. “about” sounds like “aboot”)
- Blend of British and American influence
🇦🇺 Australian English Accents
1. Broad Australian
- Region: Rural areas
- Features: Strong nasal tones, relaxed vowels
2. General Australian
- Region: Most urban areas
- Features: Neutral, slightly nasal, widely accepted
3. Cultivated Australian
- Region: Historically upper-class areas
- Features: Closer to British RP
🇳🇿 New Zealand English
- Region: Nationwide
- Features: Flat vowels, clipped words
- “Fish and chips” may sound like “fush and chups”
🇮🇪 Irish English Accents
1. Dublin Accent
- Urban, fast-paced, mix of traditional and modern
2. Belfast / Northern Irish Accent
- Sharp consonants, musical rhythm
3. Cork & Limerick
- Strong intonation, thick vowels, Gaelic remnants
🧭 Other English Accents Around the World
| Region | Accent Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| India | Indian English | Rhotic, British vocabulary, unique rhythm |
| South Africa | South African English | Dutch-influenced, variable vowel sounds |
| Jamaica | Jamaican Patois / English | Creole-influenced, rich slang |
| Nigeria | Nigerian English | British-based, rhythmic speech patterns |
| Philippines | Philippine English | American-influenced, syllable-timed |
| Singapore / Malaysia | Singlish / Manglish | Creole + English + local language mix |
BONUS: GET Free Accent Challenge
Get our accent challenge and see how familiar you are with English Accents:
🎓 Which Accent Should You Learn?
There’s no “best” accent — it depends on your goals:
- For global business or media: General American or Received Pronunciation (RP)
- For studying in the UK: RP or regional British exposure
- For working in Australia or Canada: Local variety familiarity is key
- For being understood globally: Clear pronunciation > native-sounding accent




